By: CS2103T-W16-4 Since: Feb 2020 Licence: MIT
1. Setting up
Refer to the guide here.
2. Design
2.1. Architecture
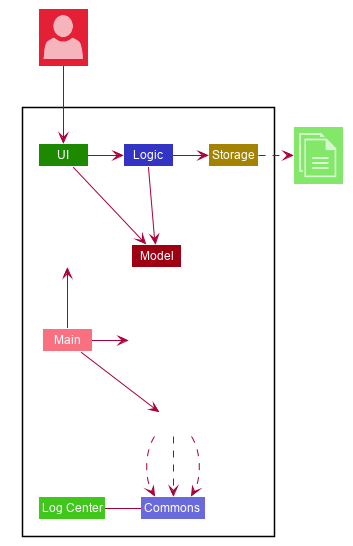
The Architecture Diagram given above explains the high-level design of the App. Given below is a quick overview of each component.
The .puml files used to create diagrams in this document can be found in the diagrams folder.
Refer to the Using PlantUML guide to learn how to create and edit diagrams.
|
-
At app launch: Initializes the components in the correct sequence, and connects them up with each other.
-
At shut down: Shuts down the components and invokes cleanup method where necessary.
Commons represents a collection of classes used by multiple other components.
The following class plays an important role at the architecture level:
-
LogsCenter: Used by many classes to write log messages to the App’s log file.
The rest of the App consists of four components.
Each of the four components
-
Defines its API in an
interfacewith the same name as the Component. -
Exposes its functionality using a
{Component Name}Managerclass.
For example, the Logic component (see the class diagram given below) defines it’s API in the Logic.java interface and exposes its functionality using the LogicManager.java class.
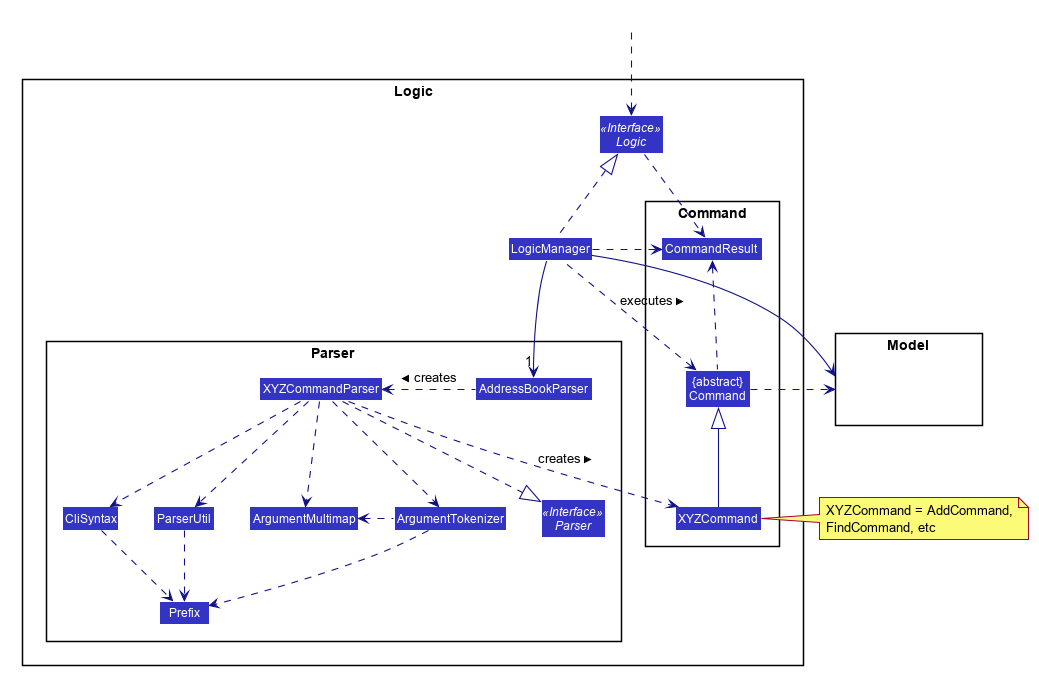
How the architecture components interact with each other
The Sequence Diagram below shows how the components interact with each other for the scenario where the user issues the command moduleAdd m/CS2103T.
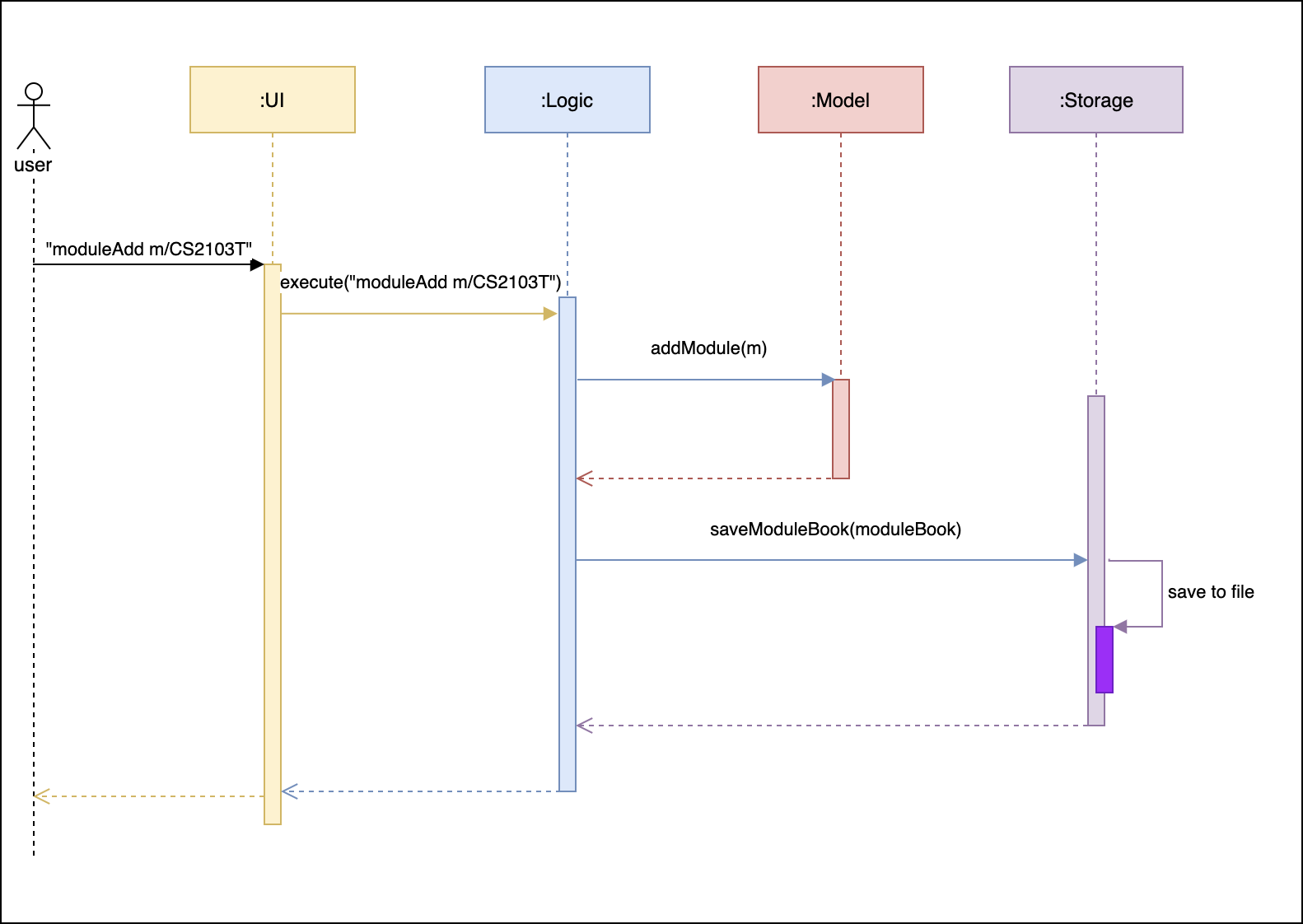
moduleAdd m/CS2103T commandThe sections below give more details of each component.
2.2. UI component
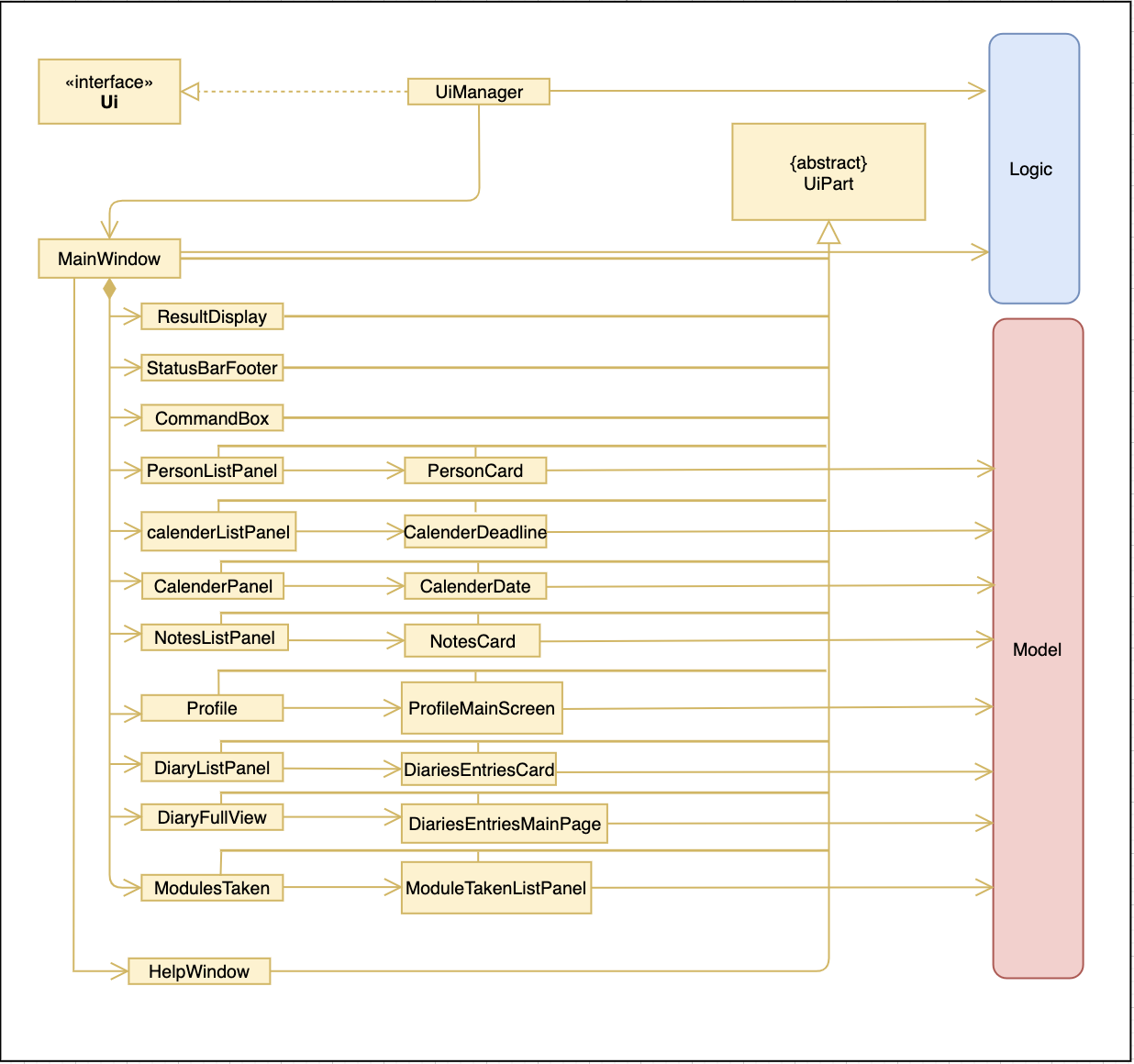
API : Ui.java
The UI consists of a MainWindow that is made up of parts e.g.CommandBox, ResultDisplay, CalendarListPanel, StatusBarFooter etc. All these, including the MainWindow, inherit from the abstract UiPart class.
The UI component uses JavaFx UI framework. The layout of these UI parts are defined in matching .fxml files that are in the src/main/resources/view folder. For example, the layout of the MainWindow is specified in MainWindow.fxml
The UI component,
-
Executes user commands using the
Logiccomponent. -
Listens for changes to
Modeldata so that the UI can be updated with the modified data.
2.3. Logic component

API :
Logic.java
-
Logicuses theAddressBookParserclass to parse the user command. -
This results in a
Commandobject which is executed by theLogicManager. -
The command execution can affect the
Model(e.g. adding a person). -
The result of the command execution is encapsulated as a
CommandResultobject which is passed back to theUi. -
In addition, the
CommandResultobject can also instruct theUito perform certain actions, such as displaying help to the user.
Given below is the Sequence Diagram for interactions within the Logic component for the execute("delete 1") API call.
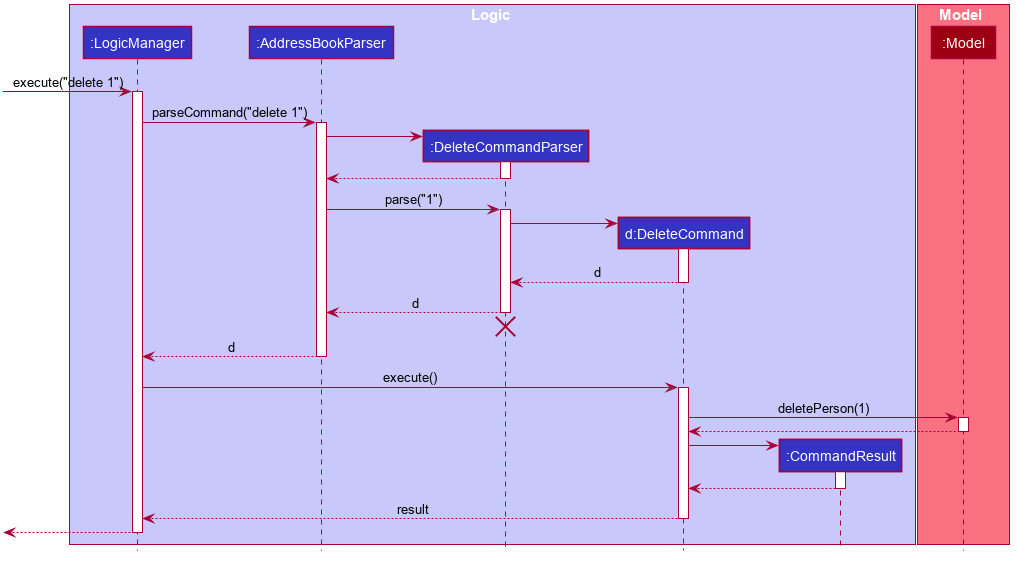
delete 1 Command
The lifeline for DeleteCommandParser should end at the destroy marker (X) but due to a limitation of PlantUML, the lifeline reaches the end of diagram.
|
2.4. Model component
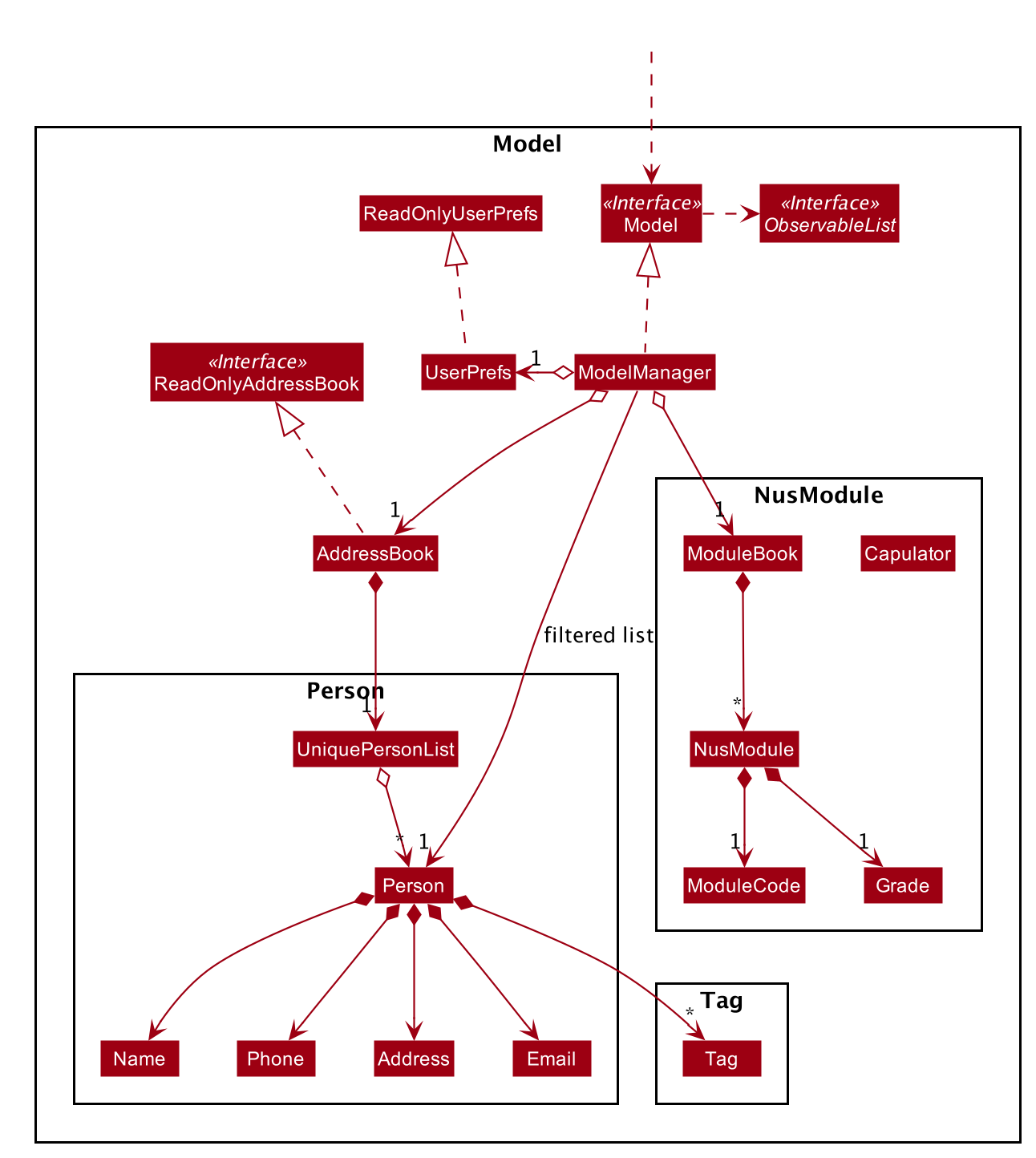
API : Model.java
The Model,
-
stores a
UserPrefobject that represents the user’s preferences. -
stores the Address Book data.
-
exposes an unmodifiable
ObservableList<Person>that can be 'observed' e.g. the UI can be bound to this list so that the UI automatically updates when the data in the list change. -
does not depend on any of the other three components.
As a more OOP model, we can store a Tag list in Address Book, which Person can reference. This would allow Address Book to only require one Tag object per unique Tag, instead of each Person needing their own Tag object. An example of how such a model may look like is given below.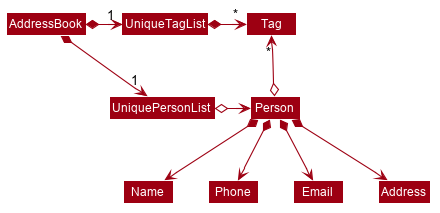
|
2.5. Storage component
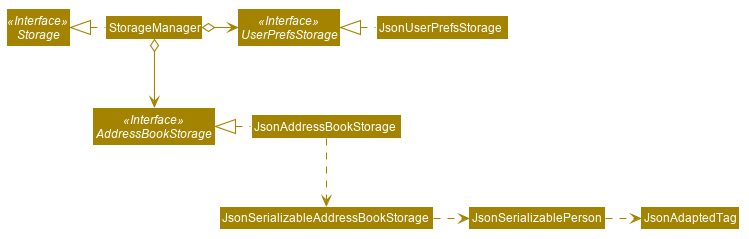
API : Storage.java
The Storage component,
-
can save
UserPrefobjects in json format and read it back. -
can save the Address Book data in json format and read it back.
2.6. Common classes
Classes used by multiple components are in the seedu.addressbook.commons package.
3. Implementation
This section describes some noteworthy details on how certain features are implemented.
3.1. Module Search
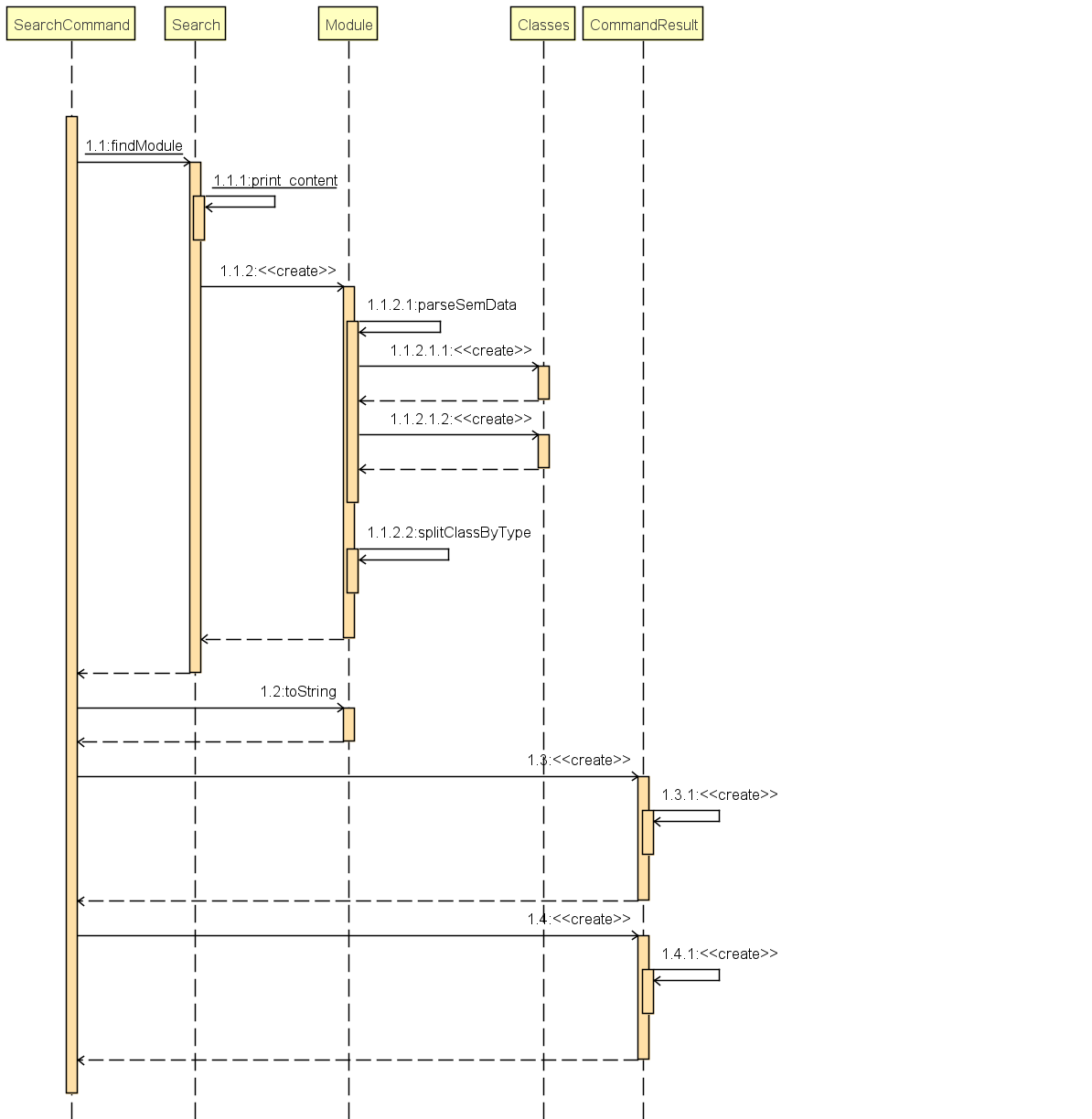
API :
Search.java
Module Search function returns module object that contains useful information for each module for the rest of the application to use.
The function first checks if the information is available in local cache, and if it isnt, pulls it from NUSmods API.
The JSON object pulled from the web is then parsed into a module object.
This implementation means that a local cache of the added modules will be available even if the user is offline.
3.2. Profile (Module Book) feature (Wangkai)
This profile feature allows users to manage the modules they have taken before or is taking now in NUS. In details, users are able to store their module taken into the program with the grades for each module stated if applicable and can also store tasks which are related to each module.
3.2.1. Implementation
-
This feature is implemented using a panel on the main screen of profile tab with a list of modules that is updated with every command that may affect module list (such as add, delete or grade).
-
The module book (profile) currently supports following features.
-
Adds in or deletes modules and display the list of modules in profile tab.
-
Updates user’s grades for each module and get CAP calculated immediately.
-
Manage the tasks related to each module (module tasks) through CLI.
-
Any modification to module tasks will be updated in the Calendar tab and also show messages on the result display panel.
-
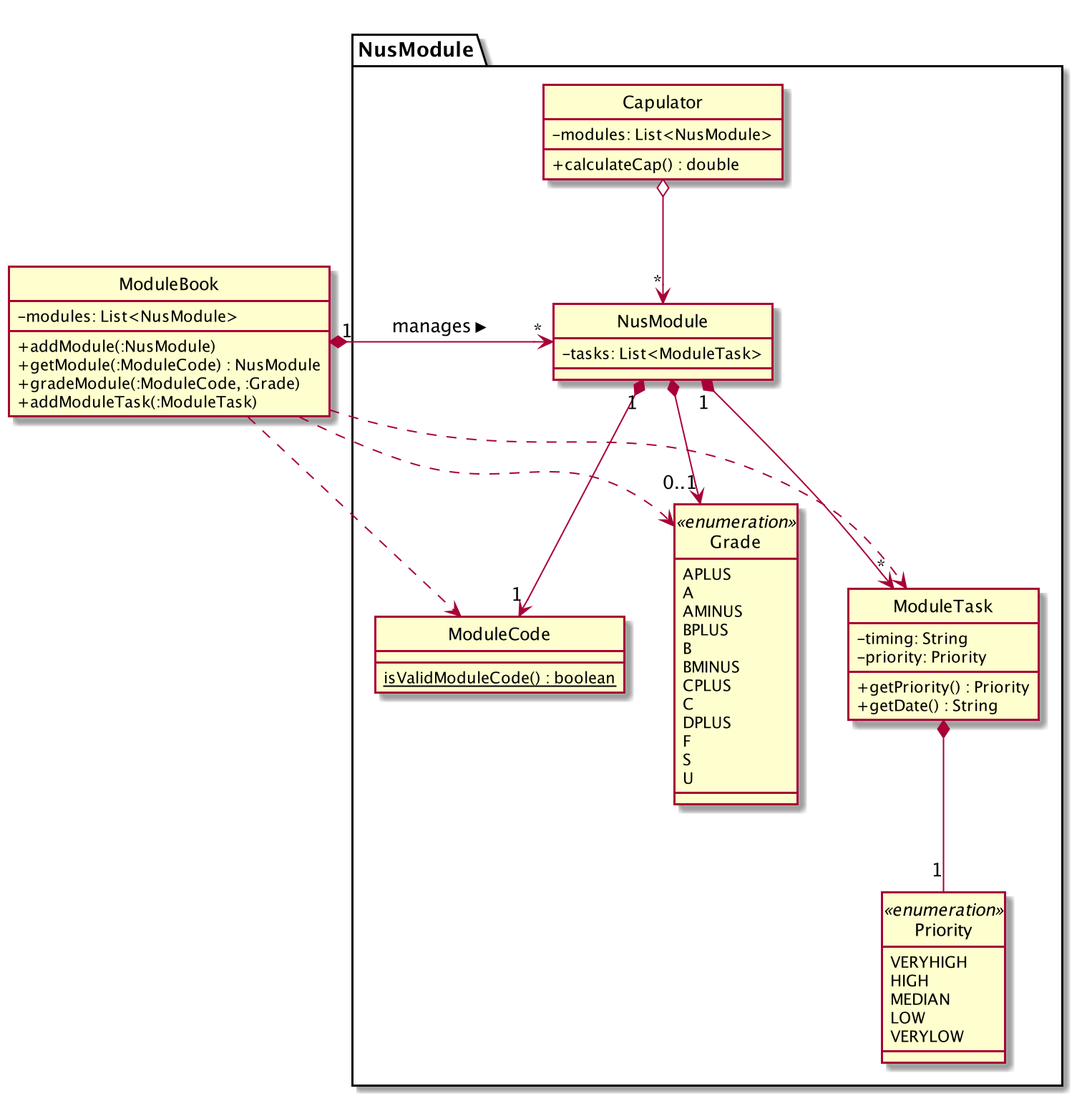
-
As shown in the class diagram above, modules are created by a class called
NusModule. Every instance ofNusModulecontains aModuleCodeobject, aGradeobject (optional) and a list ofModuleTaskobjects. -
GradeandPriorityare enumerations.Gradecontains all possible grades student can get in NUS. EveryModuleTaskinstance has aPriorityattribute which indicates how important it is.
| The module book only accept modules that are provided in NUS and will check the module code the user want to add is valid or not by using the search feature mentioned above. |
-
All possible actions mentioned above such as creating modules, deleting modules and adding tasks to modules are implemented through the
ModuleBookclass by calling corresponding methods of it such asaddModule,getModule. -
The program will automatically save any modification to module book after each command is executed by calling the
saveModuleBookmethod inStorage. -
For example, modules are created with
moduleAddcommand, followed by the module code and grade. (if applicable)
Our program will check if the module code is valid by using the search feature above and whether the module has already been added in our module book. And then call methodaddModuleinModuleBookto create the module as required. Finally, it will automatically save the module added just now. -
The Sequence Diagram below shows how the components interact with each other for the scenario where the user want to add a module in our program.
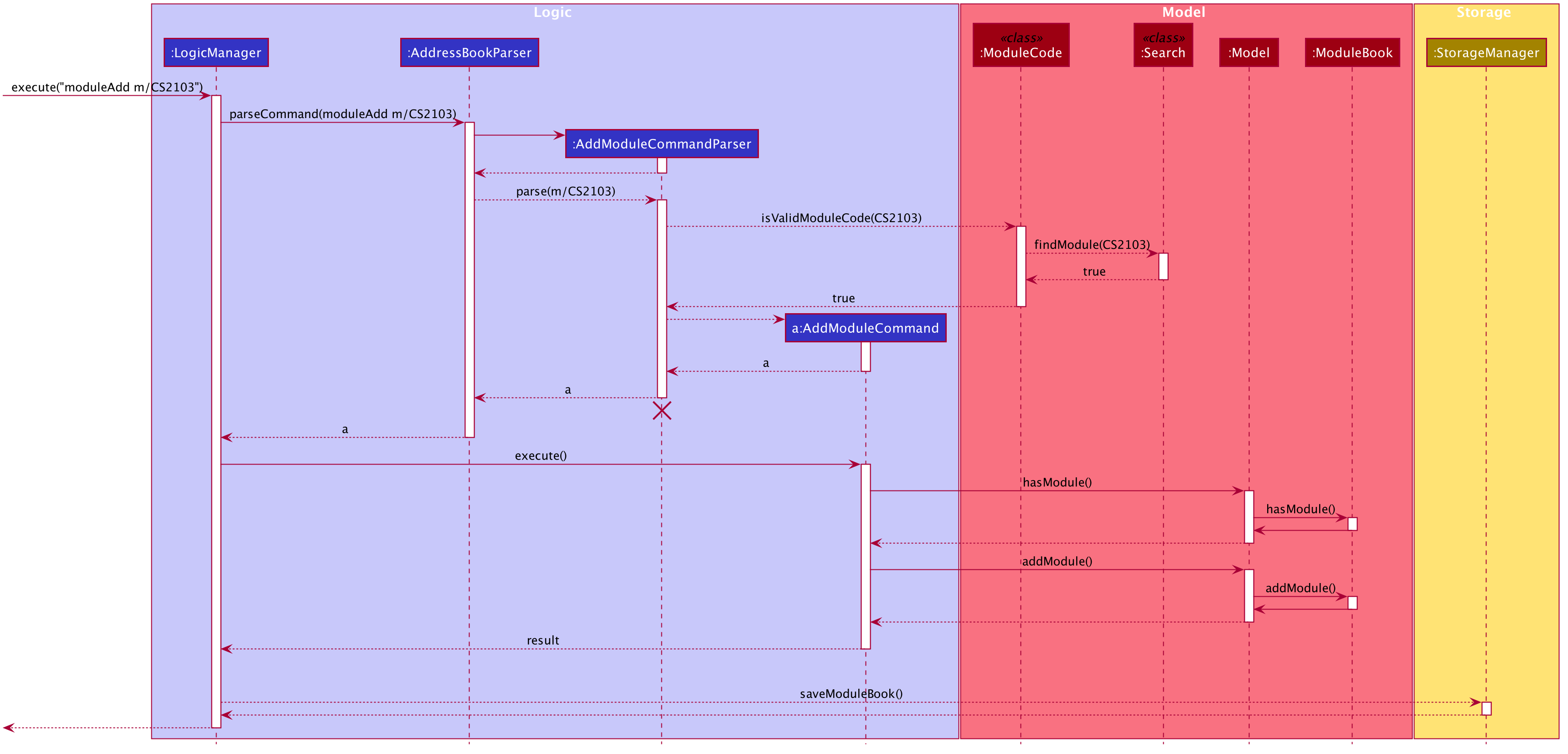
-
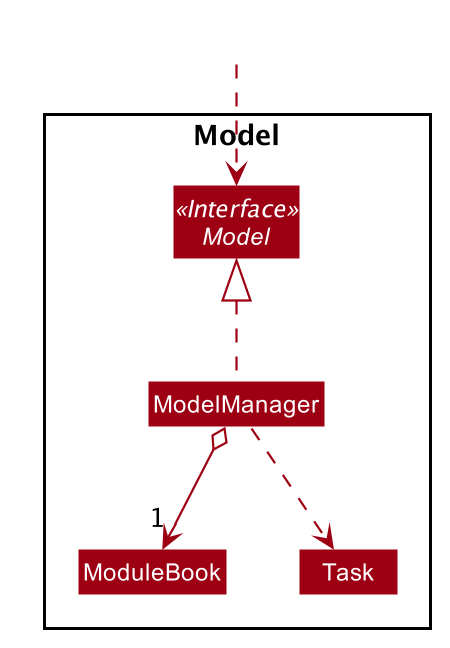
The program will synchronize the modification to module tasks in
ModuleBookwith that shown in Calendar tab throughModelManageras shown above. i.e. Any modification in module tasks will be updated inTaskwhich is the main class Calendar feature depends on. (see more details in Calendar feature)
3.2.2. Example Use Scenario
Given below are example usages scenario and how the Module Book feature behaves at each step.
| User can manage their tasks in different ways. |
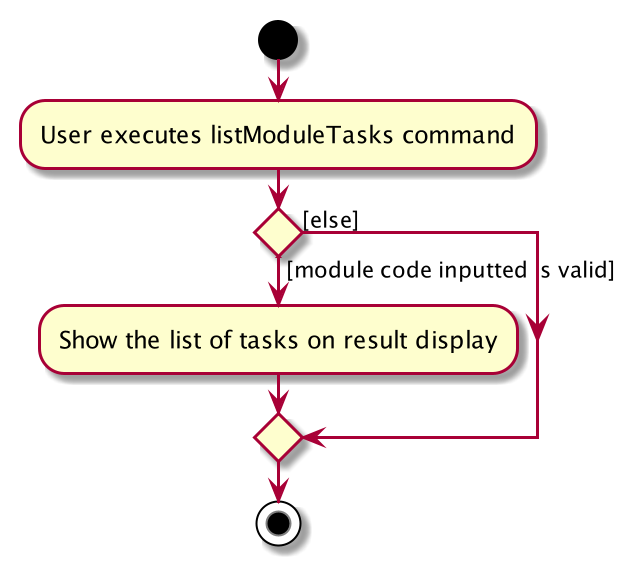
Example 1:
-
The user execute
listModuleTaskscommand. -
The program check whether the module code provided has been recorded or not.
-
Display the list of tasks.
Below is an activity diagram describing the events that will happen:
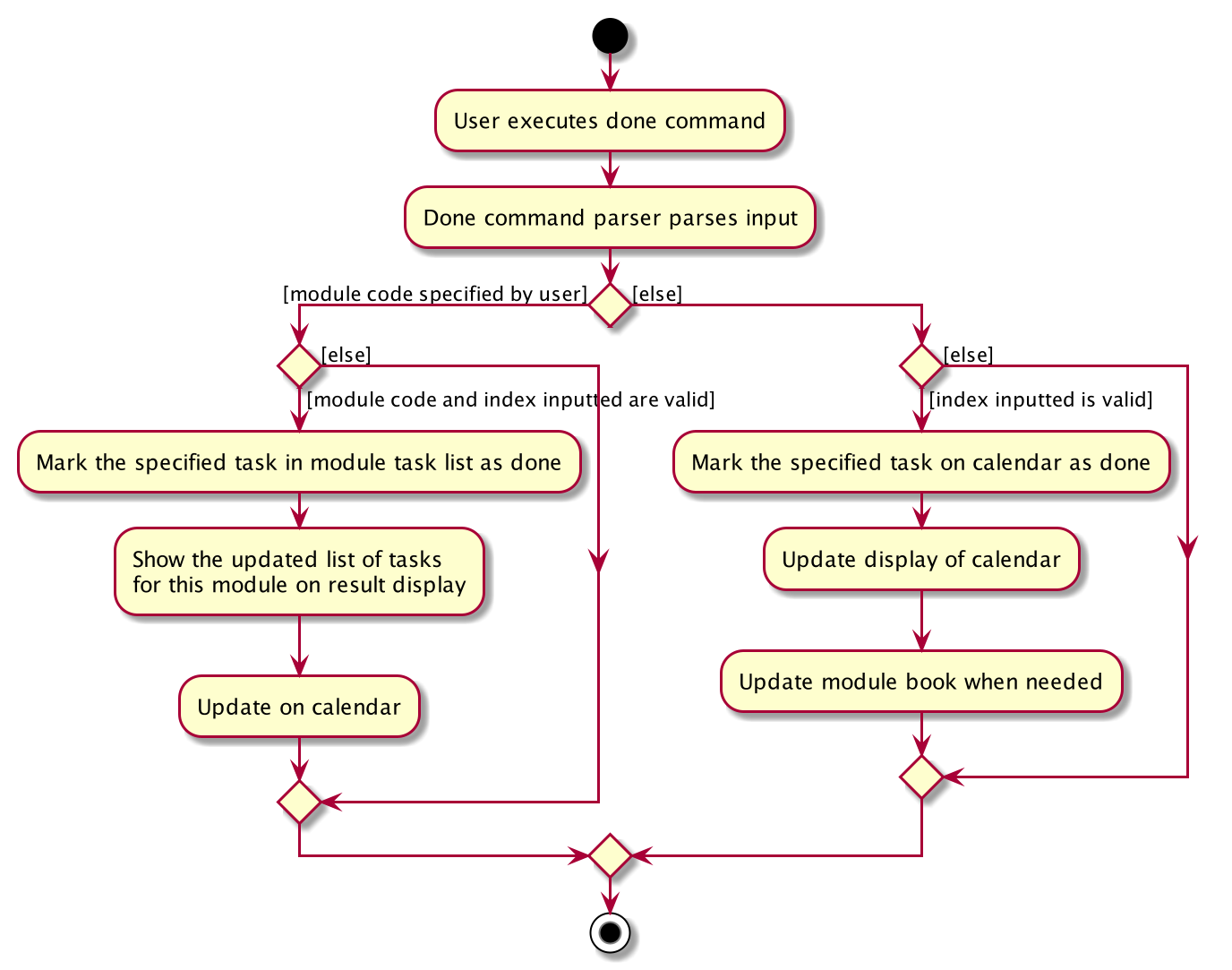
Example 2:
-
The user execute
donecommand. -
The program check whether the input is valid or not.
-
The task specified will be deleted accordingly.
-
Synchronize between module book and calendar.
Below is an activity diagram describing the events that will happen:
3.2.3. Design Considerations
Aspect 1: How the user add in a module into module book for future management ?
-
Current solution: Only need to provide the module code to add module and it will fetch the information about the module using Module Search feature automatically.
-
Pros: Users don’t need to provide any other information (such as modular credit of the module) for other functionality such as calculating the CAP.
-
Pros: The module information will be cached locally after you add the module once and this can used for future development.
-
Cons: Need Internet connection when you add in certain module for the first time.
-
Cons: Highly depends on the Module Search feature.
-
-
Alternative Solution: Let the user enter all information required for each module when they add it in. (such as modular credit)
-
Pros: More flexible, not depends on other features.
-
Cons: Very tedious for users to add in lots of modules.
-
Cons: Need to ask user to provide new information when more new functionality is added in the future.
-
Reason for chosen implementation:
The current implementation is much more user friendly and have more potential for future development. The implement can become
very ideal if the Module Search feature works properly.
Aspect 2: How the user manage their tasks for each module?
-
Current solution: For each module added, it contains a list of
ModuleTask. Also update the calendar when add task in.-
Pros: Users can either view their tasks for each module separately or view all the tasks shown in Calendar tab.
-
Pros: More nice-looking that the user can view all the deadlines on calendar.
-
Cons: Prone to bugs during the synchronization of module book and calendar.
-
-
Alternative solution: Only store the list of
ModuleTaskin module book and do not update in Calendar tab.-
Pros: Easier to implement and can avoid some synchronization bugs.
-
Cons: Users can not gain a view of the whole pictures with all tasks shown on calendar.
-
Reason for chosen implementation:
The current implementation updates the module tasks added in onto the calender and provides the users different ways
to manage their tasks. (as a whole or separately for each module)
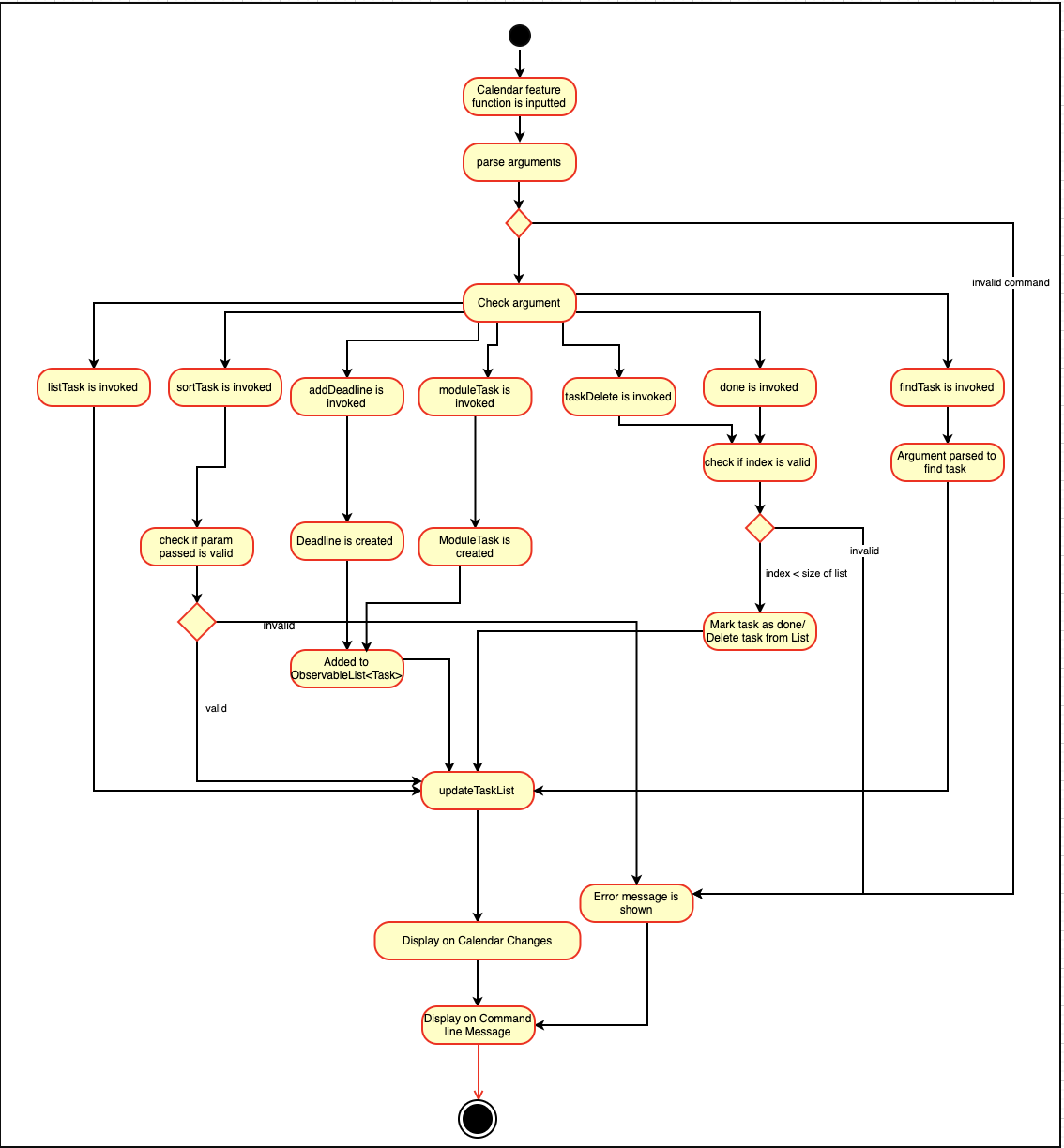
3.3. Calendar Feature (Xinwei)
NUSProductivity consist of a calendar feature that provides an overarching view of all tasks, allowing user to view their uncompleted tasks and whether there is a task present on the date itself.
The calendar feature allows users to add either a deadline or a Module Task to the calendar, which inherits from a super class Task
3.3.1. Implementation
The implementation of the main Calender tab is facilitated a SplitPane in the MainWindow class consisting of 2 main classes, CalenderListPanel and CalenderPanel
The CalenderListPanel on the right contains a list of Task added to the calendar will the CalenderPanel shows the actual calender view for the current month.
The diagram below describes the class structure of the calendar class structure.
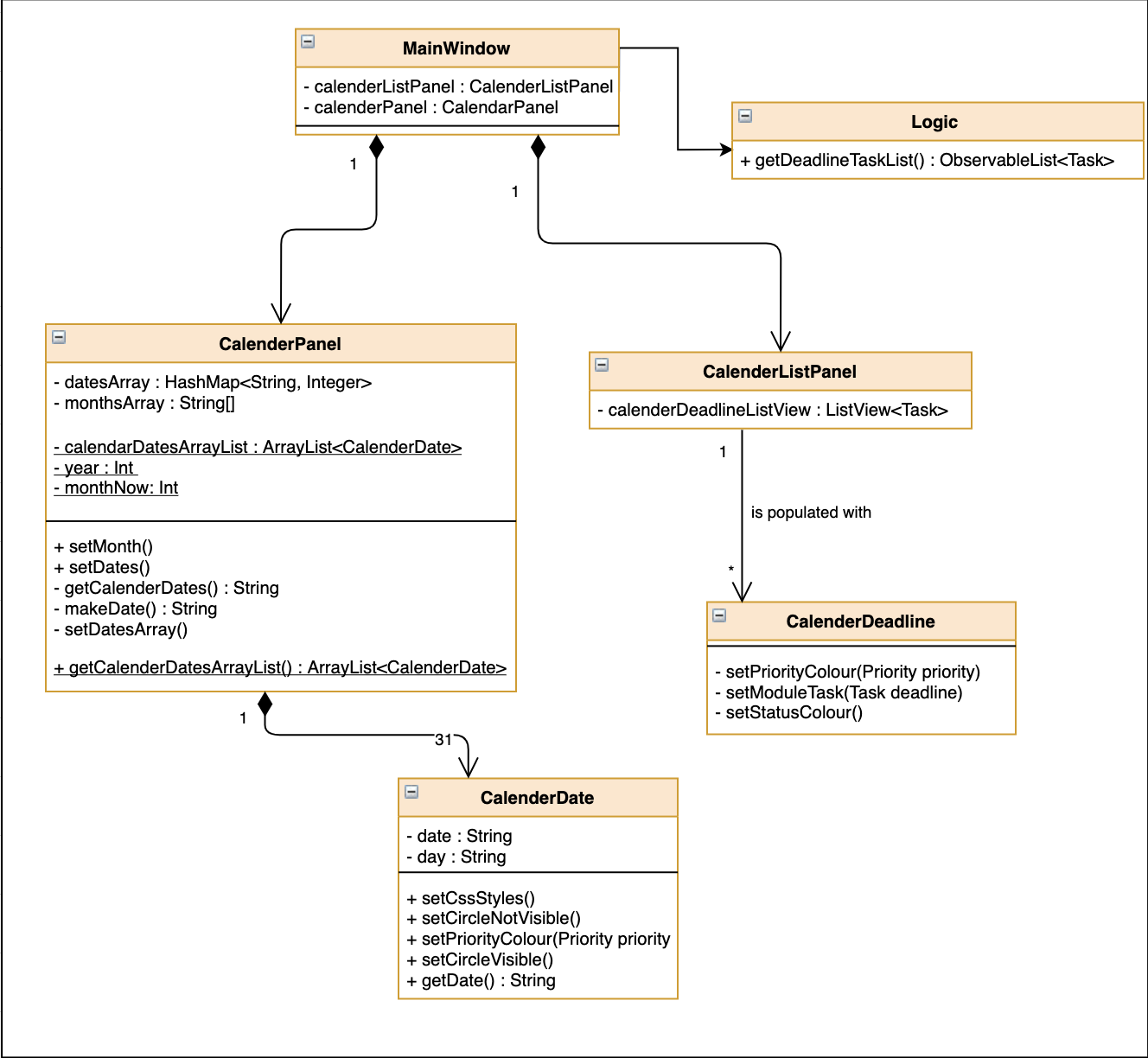
Upon initialisation of CalenderPanel, the CalenderPanel would call its 2 methods of setMonth() and setDate() to create CalenderDate instances starting from the first day of the current month.
Then, upon initialisation of CalenderListPanel, it will create instances of CalenderDeadline by getting the ObservableList<Task> from getDeadlineTaskList.
This will call upon the inner class in CalenderListPanel, DeadlineListViewCell updateItem method which allows the program to check whether there is any deadline due on any on the date in calenderDatesArrayList.
If a deadline or a Module Task is found, setPriorityColour() and setStatusColour() will be invoked to update the Calendar display to change the colour of the dots based on the priority levels mentioned in the User Guide.
Every time a Task is modified, the DeadlineListViewCell updateItem method will be invoked to update any changes to the display.
3.3.2. Implementation logic
-
Implementation: both deadline and module Task are inherits from the super class Task. A task is created when the
moduleTaskordeadlineAddcommand is invoked. -
The Sequence Diagram below shows how the components interact with each other for the scenario where the user wants to add a task to the program.
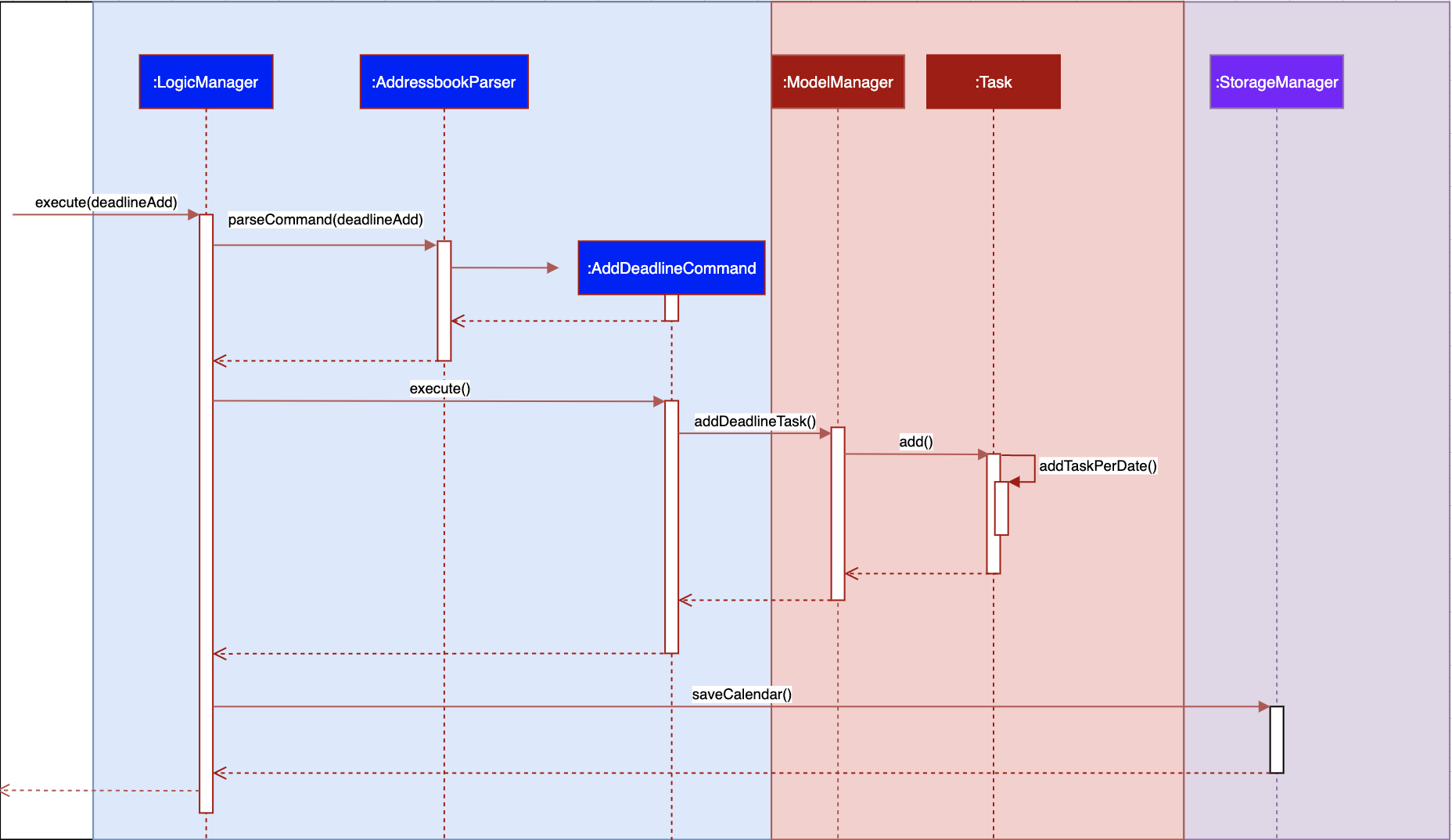
The addDeadlineTask method will modify the ObservableList<Task> supplied to the CalenderListPanel, invoking the updateItem method, causing a change in the user display.
All other calendar functions works similarly to addDeadlineTask as shown in the Activity diagram below.
3.3.3. Design Considerations:
Aspect 1: Method of displaying the dot indicator
-
Current solution: Currently, the dot is being shown by getting the
static HashMapfromTaskas thisHashMapstores a key-pair value of date - Tasks. -
By making changes to the
deadlineTaskList, we also edited theHashMap. This allows everytime aupdateItemmethod call to check whether a task is present, and if so the priority of the task. -
Alternative 1: Store all tasks of the current date in
CalendarDate.-
Pros: Allows for tasks to be accessed locally and not through a static variable from the main class
Task. -
Cons: Implementation may be more complex as more parameters have to be passed to
CalenderDateand also ensuring that the list of task passed inCalendarDateis up to date.
-
Reason for chosen implementation:
The current solution is easier to implement as everything is done in the relevant functions such as deadlineAdd or taskDelete. The only thing that the program needs to check is whether a date in the HashMap contains a task and if so, the priority of the task. With the alternative implementation, we will need to pass in a List for each of the 31 dates which may be very troublesome to keep track of especially when we are editing the main task list. This ease of implementation is the deciding factor when choosing which method to implement.
3.4. Notes Feature (Xinwei)
3.4.1. Implementation
The notes feature allow users to access their desktop files and folders with commands.
This feature is implemented using a panel on the main window, listing out a list of documents and folders that are in the specified directory.
Notes features includes notesOpen, notesCreate, notesDelete and notesList.
The diagram below shows the sequence diagram of a notesOpen command with the other methods working similarly to the stated method.
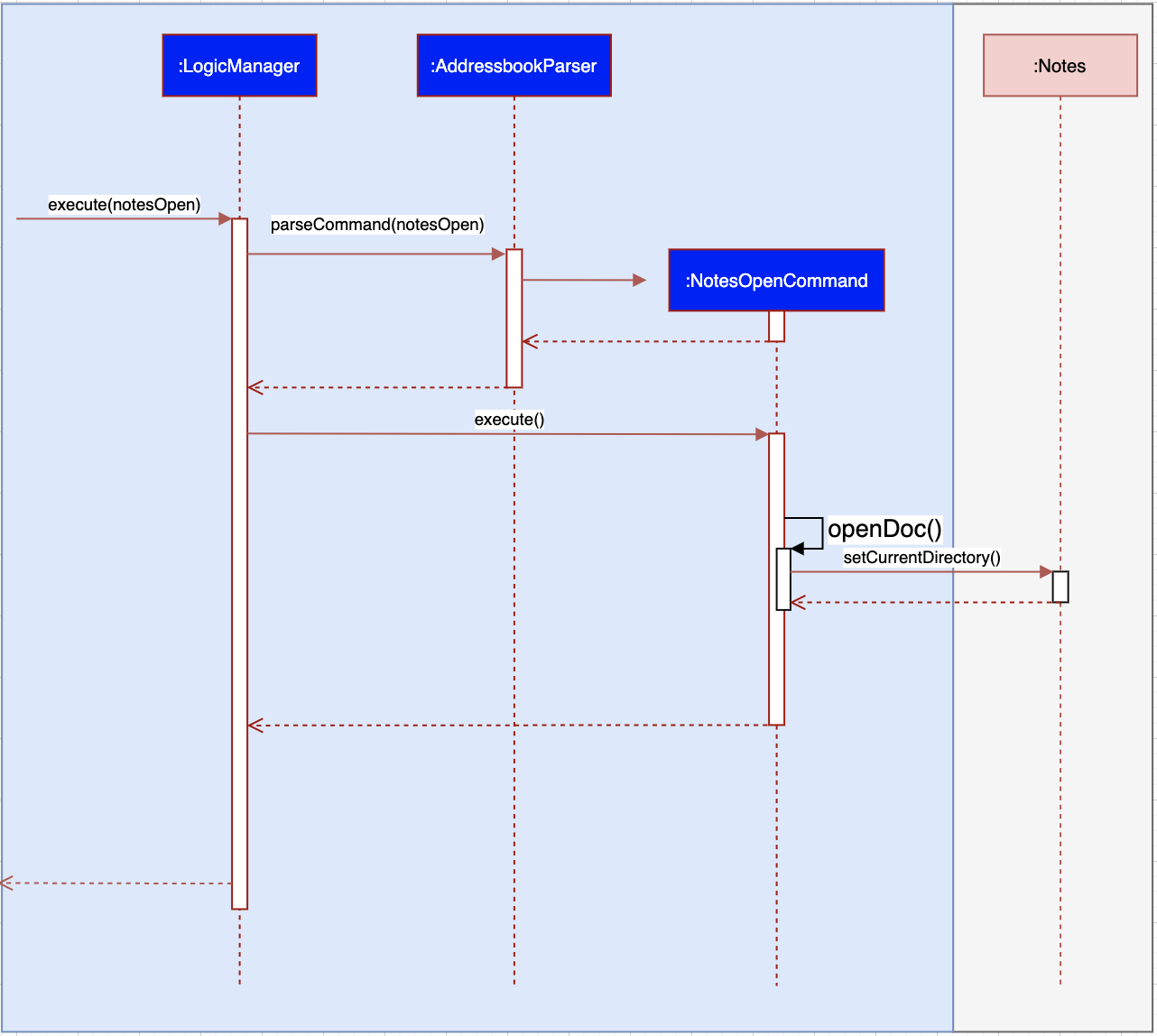
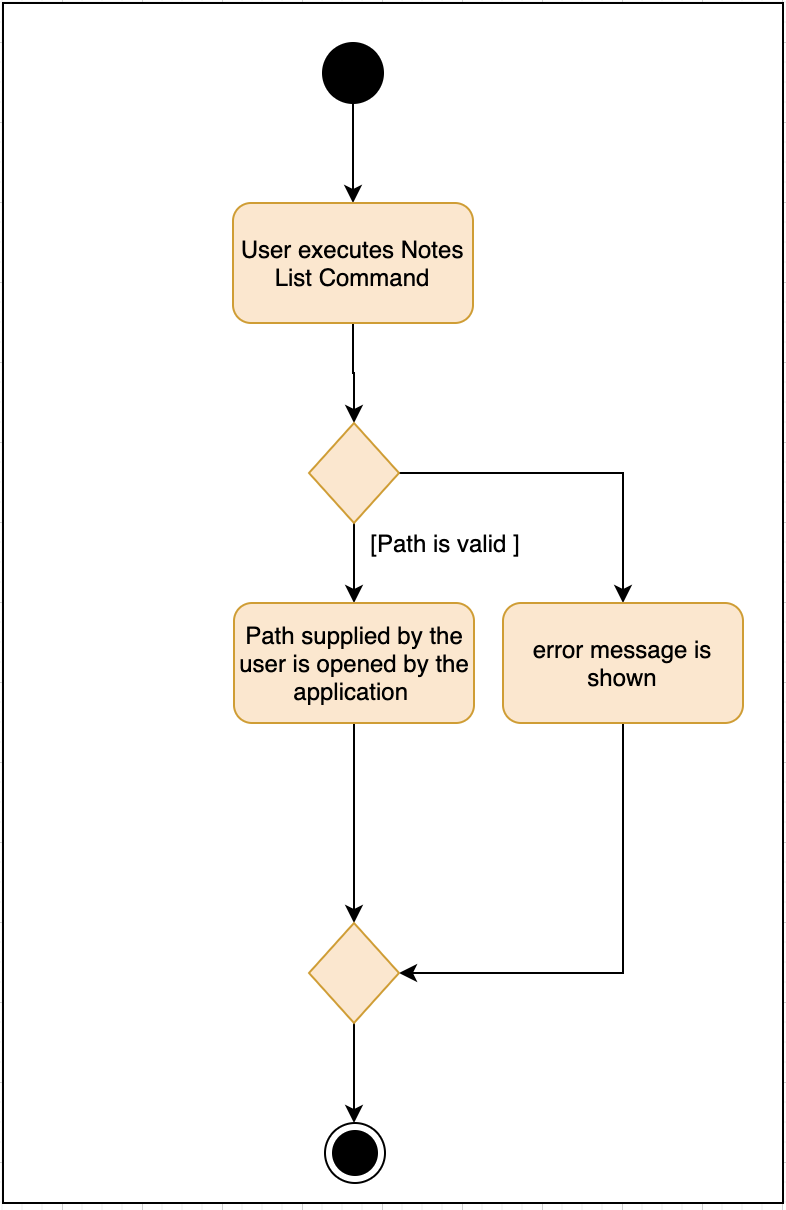
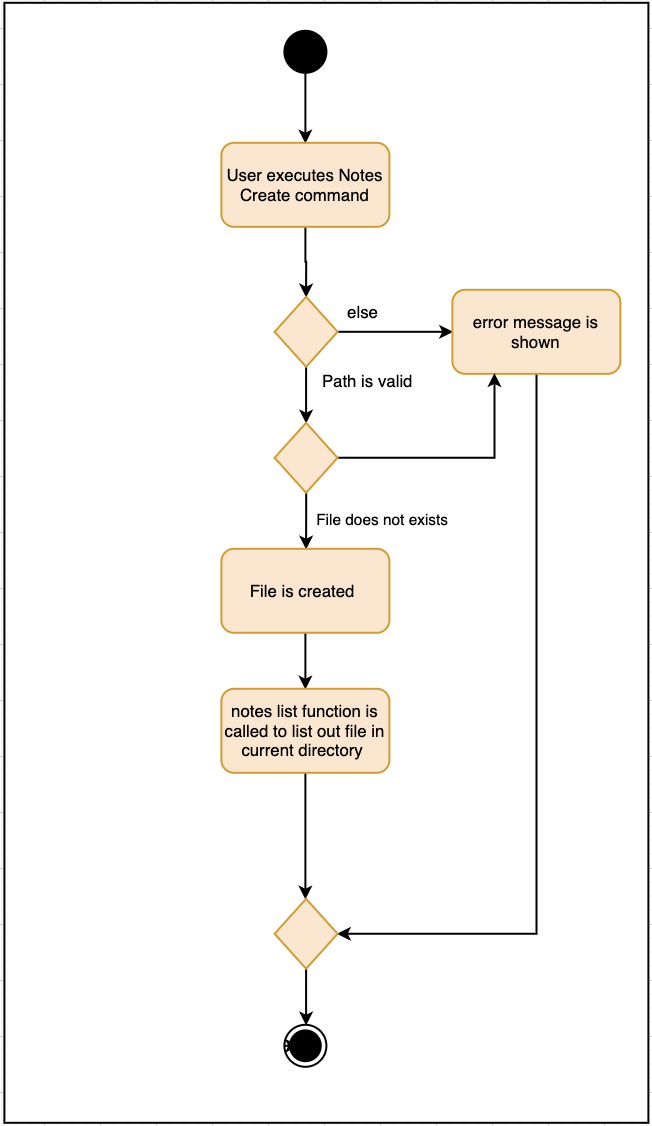
notesCreate and notesDelete activity diagram works similar to notesOpen.
3.4.2. Pathing
Our program allows the user to specify different pathing system, namely:
-
AbsolutePath
-
RelativePath
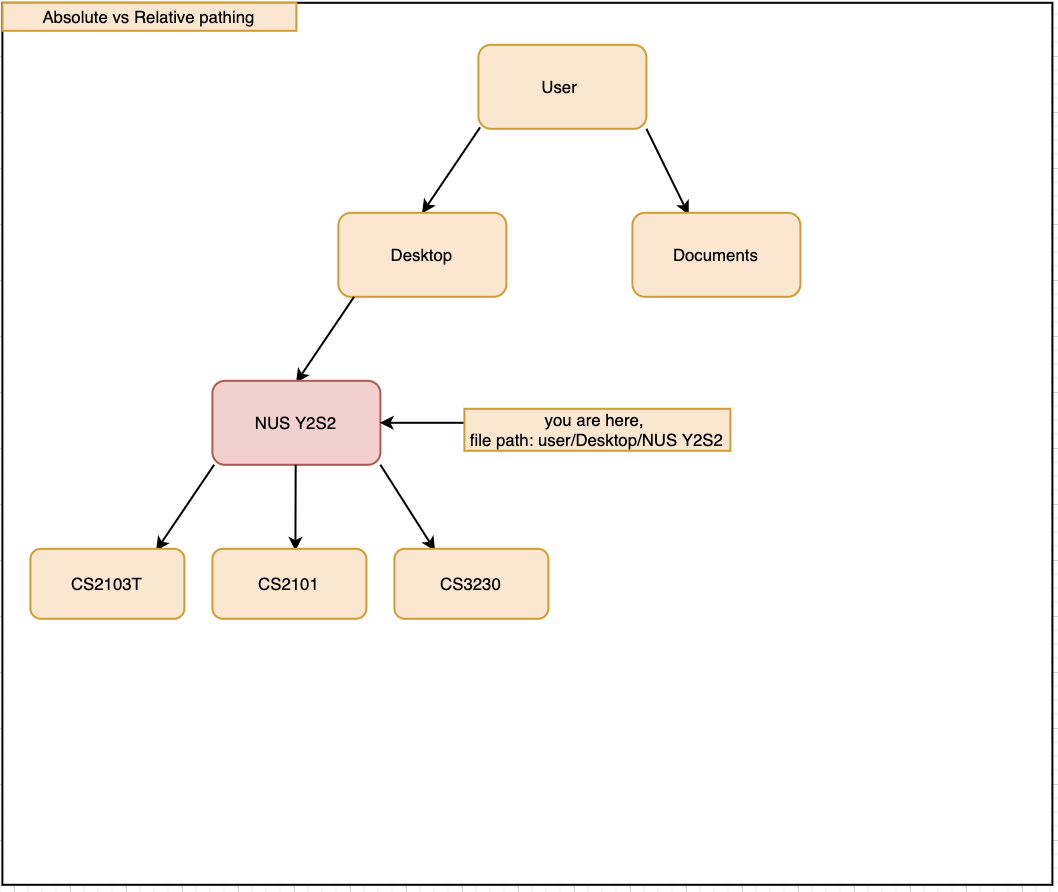
AbsolutePath will take the path given from usr/.
RelativePath will take reference from the path that the current system has opened, in this case, usr/Desktop/NUS Y2S2.
The user is given the freedom to provide any of the 2 forms when using the notesOpen, notesCreate, notesDelete and notesList commands.
AbsolutePath:
Benefits:
This allows for more flexibility as the user do not need to keep note of its current directory and will be able to access any folder/document that is on their system
cons:
Will require much more input from the user, for example, referring to the above figure,
Accessing the CS2103T file requires the user to input loc/Desktop/NUS Y2S2/CS2103T as opposed to loc/CS2103T if the user is using absolute over relative pathing
RelativePath:
Benefits:
Easier for the user to navigate through the current folder and not key in the whole folder path
Cons:
Not as flexible. Referring to the above diagram,
Accessing the Documents folder will require the user to input loc/../../Documents, this may not be as intuitive to people with no programming background.
Using loc/Documents abs/abs will allow the user to access any folder from anywhere.
3.5. Diary feature (Jiangwei)
The diary feature is just like a real life diary book. It allows you jot down any thoughts, be it for your personal life or for school work. You can also note down a concept you don’t understand or your reflection for each day in case you want to revisit them in the future. In details, users can add and delete a diary entry, display a particular diary entry and tag each entry with mood or the weather on that day.
3.5.1. Implementation
-
This feature is implemented using a panel on the main screen of diary tab. The list of diary entries will update upon executing diary commands that may affect Diary Book. (such as diaryAdd, diaryDelete or diaryMood) The GUI aspect is not fully implemented yet (coming in v2.0), so the current implementation’s response is in CLI style.
-
The Diary Book currently supports the following features:
-
Adding a diary entry
-
Deleting a diary entry
-
Showing the log of recorded entries
-
Display a particular diary entry with specified entry ID
-
Finds the list of diary entries the match a given date
-
tagging a entry with mood or weather
-
-
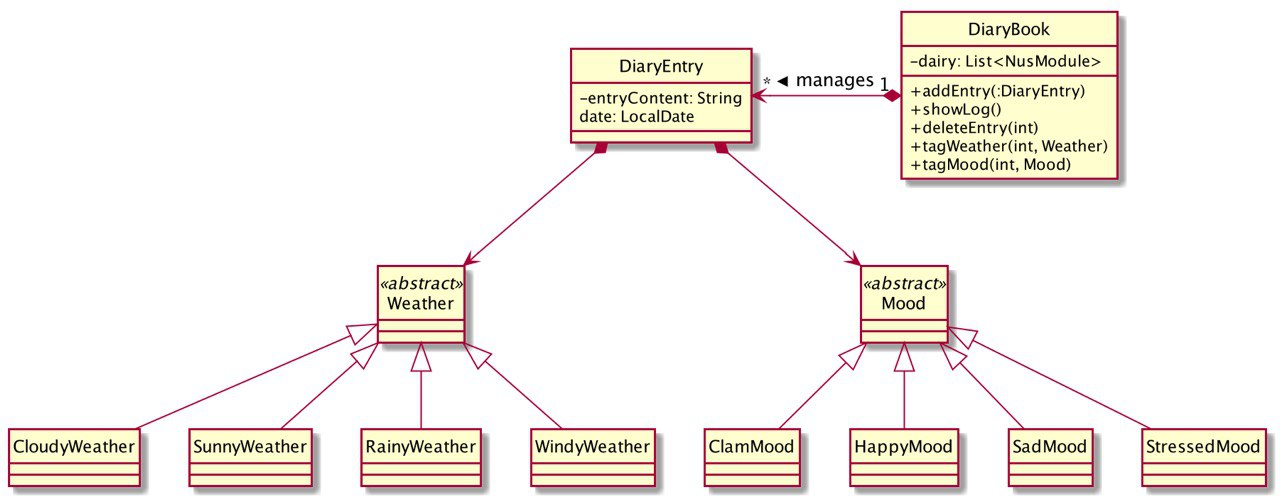
As shown in the class diagram above, diary entries are created by
DiaryEntryclass. Every instance ofDiaryEntrycontains aLocalDate, aMoodobject (optional) and aWeatherobject (optional). -
Different types of
Moodsuch asCalmMood,HappyMoodextends from the abstract classMood. Similar subtype relation holds for different types of weather and the abstract classWeather. -
List of diary entries are managed by the
DiaryBookclass. All relevant actions such as adding, deleting as described above are implemented insideDiaryBook. This can be seen from the methods ofDiaryBookin the class diagram above.
3.5.2. Example Use Case
Given below are example usages scenario and how the Module Book feature behaves at each step.
-
Example: deleting the diary entry with entry ID 1 The sequence diagram below shows how the
diaryDelete id/1command is executed
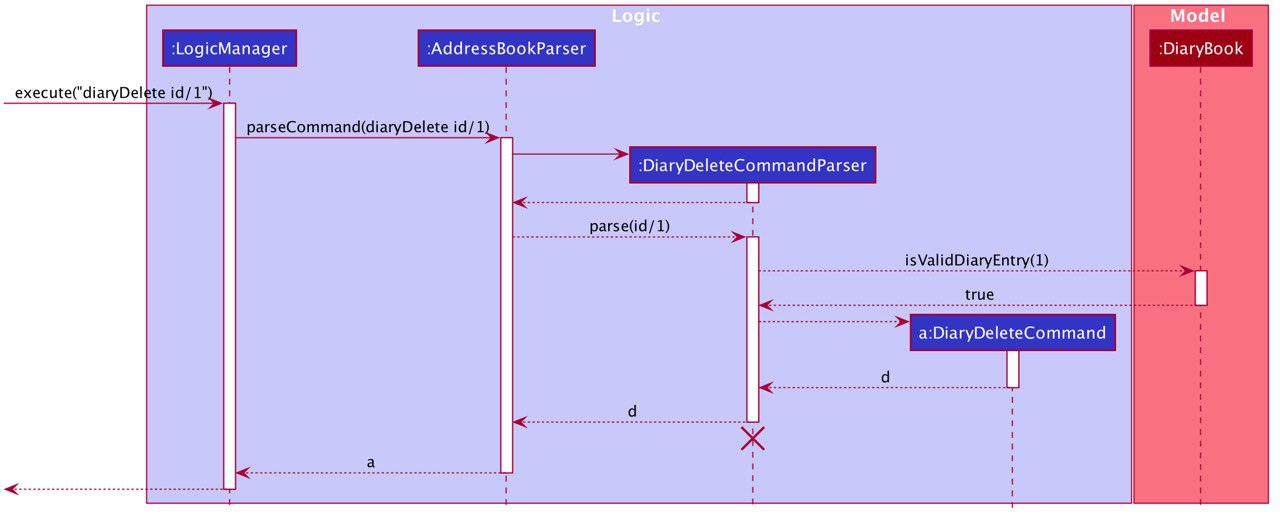
diaryDelete id/13.5.3. Design Considerations
How does the user edit a diary entry?
- Current solution: Mood and Weather can be updated easily with the diaryMood and diaryWeather command. However, We have not include a edit feature for the entry content. The users can first delete the entry and re-add the entry with updated diary entry.
Pros: May deter users from changing past diary content as diary is meant to record what have happened and editing the past experience may not be encouraged.
Cons: The users may need to retype the whole entry content which is a time consuming process.
-
Alternative solution: include a feature that replaces a certain keyword with a new keyword.
-
Pros: Requires less typing and less time consuming.
-
Cons: May cause some unintended changes to the entry content because of entry content containing substrings of the replaced keyword.
-
Reason for chosen implementation: We want to adhere to the fact that past diary entries should not be changed but still allows editing, only that it will require more effort. The alternative solution is certainly feasible, to avoid the downsides of the alternative solution we can incorporate regular expressions to ensure more accurate replacing. However, this may require the users to have some prior knowledge which is not desired.
3.6. Event Feature (Proposed) (Xuan Xin)
This feature (in the works already) is meant to be an enhancement towards the Calendar feature.
3.6.1. Implementation
-
The event feature would support the following features:
-
Adds and deletes events onto the calendar
-
Sort events by date (default)
-
Consolidate and list all events
-
The sequence diagram below shows how components interact with each other when user inputs eventAdd to add an event onto the calendar.
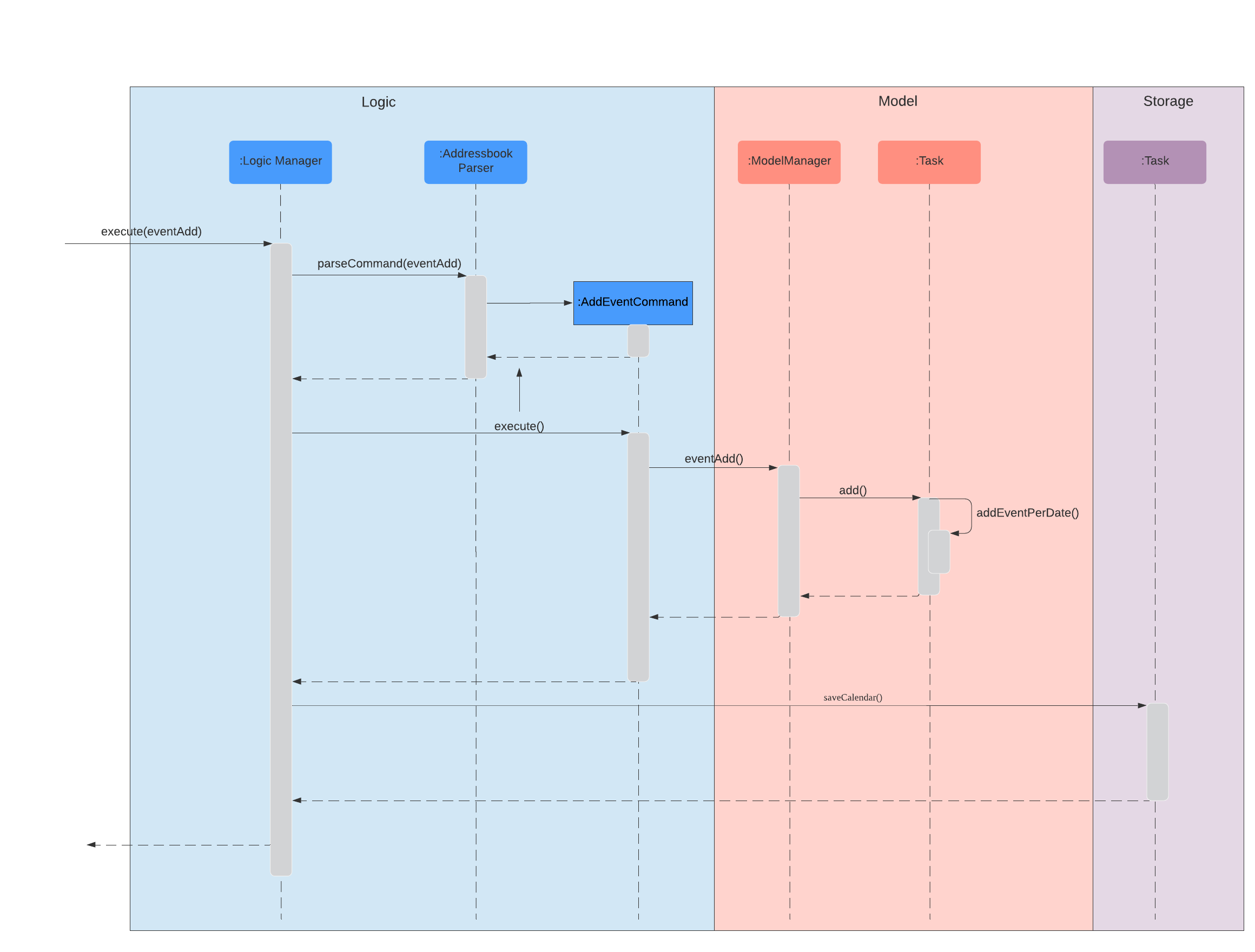
The eventAdd method works similar to the addDeadlineTask above and will modify the ObservableList<Task> supplied to the CalenderListPanel, invoking the updateItem method, causing a change in the user display.
3.6.2. Example Use Scenario
Example 1:
-
The user execute
listEventcommand. -
The program checks if input is valid.
-
The list of events will be displayed.
Below then shows an example of an activity diagram for the listEvent command.
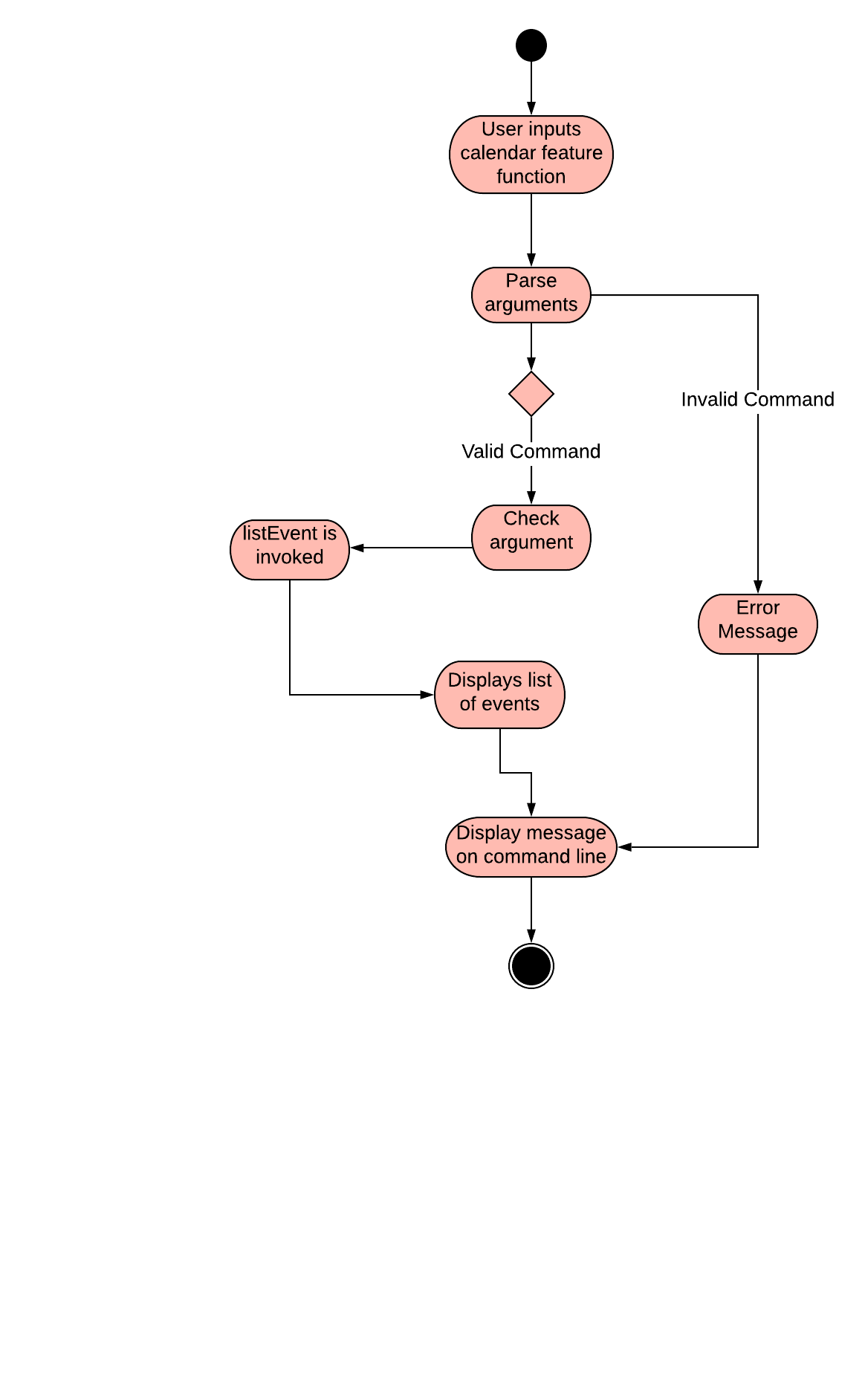
3.6.3. Further Developments
-
The event feature will aim to link contacts from the addressbook to the calendar.
For now, the full activity diagram for Event, which has a similar implementation to Deadline, is shown below:
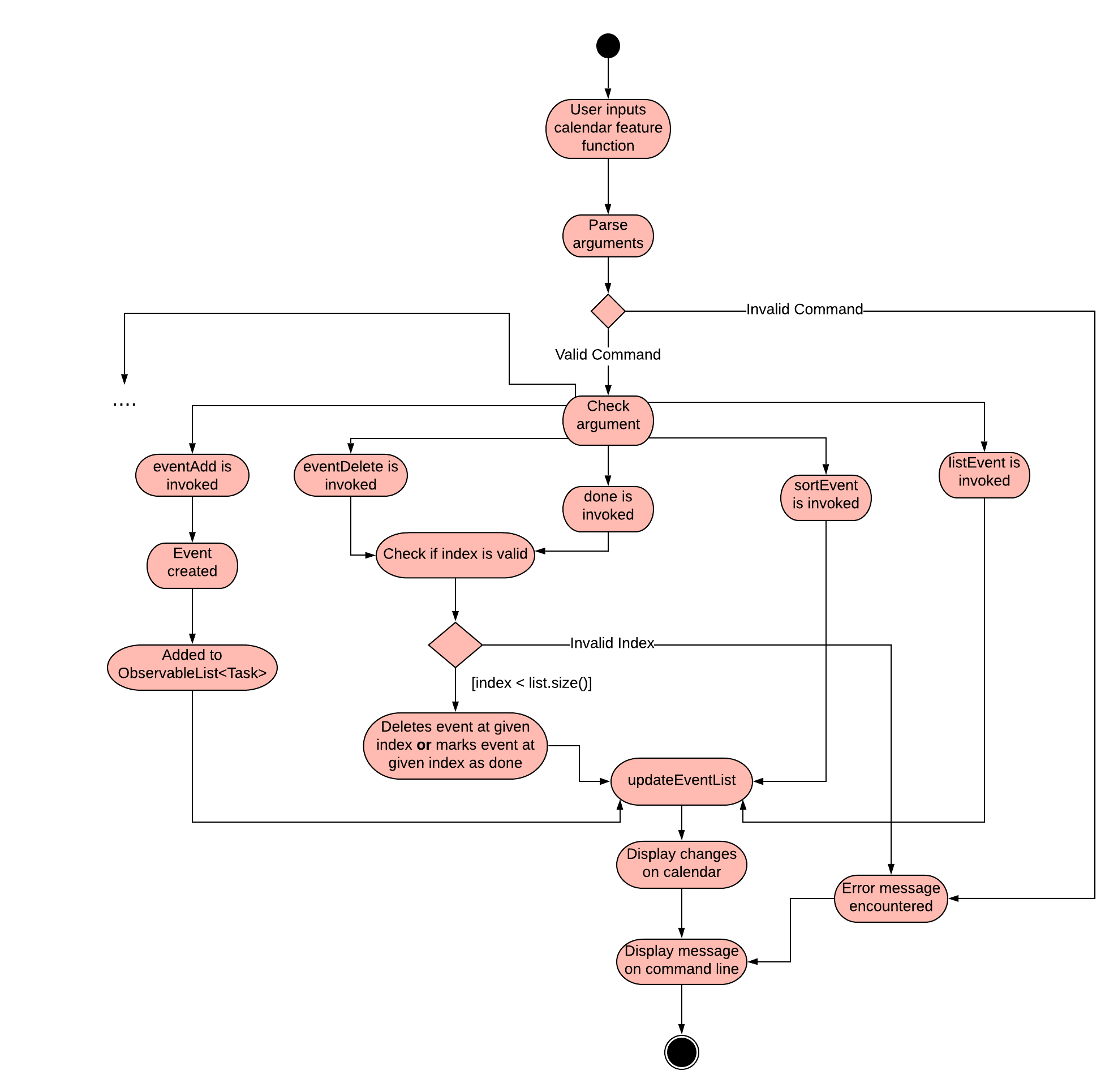
3.7. Logging
We are using java.util.logging package for logging. The LogsCenter class is used to manage the logging levels and logging destinations.
-
The logging level can be controlled using the
logLevelsetting in the configuration file (See Section 3.8, “Configuration”) -
The
Loggerfor a class can be obtained usingLogsCenter.getLogger(Class)which will log messages according to the specified logging level -
Currently log messages are output through:
Consoleand to a.logfile.
Logging Levels
-
SEVERE: Critical problem detected which may possibly cause the termination of the application -
WARNING: Can continue, but with caution -
INFO: Information showing the noteworthy actions by the App -
FINE: Details that is not usually noteworthy but may be useful in debugging e.g. print the actual list instead of just its size
3.8. Configuration
Certain properties of the application can be controlled (e.g user prefs file location, logging level) through the configuration file (default: config.json).
4. Documentation
Refer to the guide here.
5. Testing
Refer to the guide here.
6. Dev Ops
Refer to the guide here.
Appendix A: Product Scope
Target user profile:
-
has a need to manage a significant number of contacts
-
has a need to manage deadlines and tasks
-
has a need to manage module planning
-
prefer desktop apps over other types
-
prefers typing over mouse input
-
prefers to have everything in one app
-
can type fast
-
is reasonably comfortable using CLI apps
-
is studying in NUS
Value proposition: manage contacts faster than a typical mouse/GUI driven app
Appendix B: User Stories
Priorities: High (must have) - * * *, Medium (nice to have) - * *, Low (unlikely to have) - *
Priority |
As a … |
I want to … |
So that I can… |
|
new user |
see usage instructions |
refer to instructions when I forget how to use the App |
|
user |
add a new person |
|
|
user |
delete a person |
remove entries that I no longer need |
|
user |
find a person by name |
locate details of persons without having to go through the entire list |
|
user who wants to improve time management |
add deadlines |
know when to complete tasks in todo list |
|
user |
add event |
know when and where is the event and who will going to participate in the event |
|
NUS student |
add module to module plan |
see modules I need to take to fulfill degree requirements |
|
NUS student |
show module plan |
see list of modules I need to take/have taken |
|
NUS student |
write and save notes for each module I have taken/am taking |
|
|
NUS student |
write diaries for each day’s summary |
refer back to what I have done in the future |
|
user |
hide private contact details by default |
minimize chance of someone else seeing them by accident |
|
user |
delete diary entry |
|
|
user |
show diary entry list |
|
|
user |
delete module from module plan |
know which modules I have taken |
|
NUS student |
fetch module information |
|
|
NUS student |
know current CAP |
|
|
user who wants to improve grades |
calculate target CAP |
know what grades to aim for to achieve my target CAP |
|
user |
sort deadlines |
prioritize which tasks to finish first |
|
user who has a short memory span |
receive reminders about the deadlines |
don’t miss out any important tasks |
|
user with many persons in the address book |
sort persons by name |
locate a person easily |
|
user |
create group chats |
communicate with peers in the same module |
|
user |
tag my diary with that day’s weather |
|
|
user |
tag my diary with that day’s emotion |
I can filter my diaries with specific mood |
{More to be added}
Appendix C: Use Cases
(For all use cases below, the System is the AddressBook and the Actor is the user, unless specified otherwise)
Use case: Delete person
MSS
-
User requests to list persons
-
AddressBook shows a list of persons
-
User requests to delete a specific person in the list
-
AddressBook deletes the person
Use case ends.
Extensions
-
2a. The list is empty.
Use case ends.
-
3a. The given index is invalid.
-
3a1. AddressBook shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 2.
-
Use case: Delete module
MSS
-
User requests to show module plan
-
AddressBook shows module plan
-
User requests to delete a module taken
-
AddressBook deletes module
-
AddressBook updates module plan
Use case ends.
Extensions
-
3a. The given module code is invalid.
-
3a1. AddressBook shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 2.
-
{More to be added}
Appendix D: Non Functional Requirements
-
Should work on any mainstream OS as long as it has Java
11or above installed. -
A user with above average typing speed for regular English text (i.e. not code, not system admin commands) should be able to accomplish most of the tasks faster using commands than using the mouse (e.g. fetch module information)
-
Should respond within 2 seconds with exception of 5s for some commands due to network availability (
moduleSearch,moduleAdd) -
Should be easy to use for users who are novice at using technology
-
User should be a current student in NUS
{More to be added}
Appendix E: Glossary
- Mainstream OS
-
Windows, Linux, Unix, OS-X
- Private contact detail
-
A contact detail that is not meant to be shared with others
- NUS
-
National University of Singapore
- CAP
-
The Cumulative Average Point is the weighted average grade point of the letter grades of all the modules taken by the students, according to NUS’s grading system.
- CLI
-
Command Line Interface
Appendix F: Instructions for Manual Testing
Given below are instructions to test the app manually.
| These instructions only provide a starting point for testers to work on; testers are expected to do more exploratory testing. |
F.1. Launch and Shutdown
-
Initial launch
-
Download the jar file and copy into an empty folder
-
Double-click the jar file
Expected: Shows the GUI with a set of sample contacts. The window size may not be optimum.
-
-
Saving window preferences
-
Resize the window to an optimum size. Move the window to a different location. Close the window.
-
Re-launch the app by double-clicking the jar file.
Expected: The most recent window size and location is retained.
-
{ more test cases … }
F.2. Deleting a person
-
Deleting a person while all persons are listed
-
Prerequisites: List all persons using the
listcommand. Multiple persons in the list. -
Test case:
delete 1
Expected: First contact is deleted from the list. Details of the deleted contact shown in the status message. Timestamp in the status bar is updated. -
Test case:
delete 0
Expected: No person is deleted. Error details shown in the status message. Status bar remains the same. -
Other incorrect delete commands to try:
delete,delete x(where x is larger than the list size) {give more}
Expected: Similar to previous.
-
F.3. Calendar
-
Test case:
deadlineAdd desc/Test deadline date/30-04-2020 cat/Work
Expected: A deadline task is added to the list, details of the task is shown on th left hand side of the calendar tab. A green dot will appear on 30-04-2020 to show that there is a task on that day -
Test case:
deadlineAdd desc/Test deadline2 date/28-04-2020 cat/Work
Expected: A deadline task is added to the list, details of the task is shown on th left hand side of the calendar tab. The task list on the left should show list sorted by dates, i.e. this deadline to be above the test case in a. -
Test case:
moduleTask m/CS2103T desc/CS2103T Test by/04-04-2020 pri/5
Expected: An error message shown that no such module is present (if you haven’t add CS2103T to the program), else, a task will be added to the list, the task list on the left will be sorted by date and a red dot (priority = 5) will be shown on the calendar -
Test case:
taskDelete index/1
Expected: First task on the task list is deleted. -
Test case:
taskDelete index/0
Expected: No task will be deleted. Error details shown in the status message. Status bar remains the same. -
Test case:
sortTask by/priority
Expected: Task on the left is sorted by priority. -
Test case:
sortTask by/asiqowe
Expected: No sorting will be parsed and error message will be shown. Status bar remains the same. -
Test case:
findTask date/30-04-2020
Expected: All task that have a deadline of 30-04-2020 will be shown on the left panel, calendar dots for other dates will NOT be removed. -
Test case:
listTask
Expected: List all task after a findTask to show all available Tasks.
F.4. Notes
-
Test case:
notesList loc/Desktop pt/abs
Expected: All files on your desktop will be listed in the display -
Test case:
notesList loc/Desktop/Desktop by/abs
Expected: Error message will be shown -
Test case:
notesOpen loc/Desktop name/Test.doc pt/abs
Precondition: Needs to have a file called Test.doc on the desktop, else an error will be thrown
Expected: File is opened, notes user interface current directory changed to usr/Desktop -
Test case:
notesCreate loc/Desktop name/test type/folder pt/abs
Precondition: No folder on the desktop is named test
Expected: folder is created, notes user interface current directory changed to usr/Desktop/test -
Test case:
notesDelete loc/Desktop name/Test.doc pt/abs
Precondition: Needs to have a file called Test.doc on the desktop, else an error will be thrown
Expected: File is deleted, notes user interface current directory changed to usr/Desktop
F.5. Module
-
Test case:
moduleAdd m/CS2103T g/A+
Expected: A module of CS2103T with its grade will be added to the profile tab list -
Test case:
moduleAdd m/CS2103123123T g/A+
Expected: Error message will be thrown with no such module. -
Test case:
moduleAdd m/CS2101
Expected: Module of CS2101 will be added to the profile tab, without a grade. -
Test case:
moduleDel m/CS2103T
Expected: CS2103T module will be deleted -
Test case:
grade m/CS2101 g/A+
Expected: CS2101 grade will be updated to A+ -
Test case:
cap
Expected: Calculates your current cap with the modules inputted.